Cookies
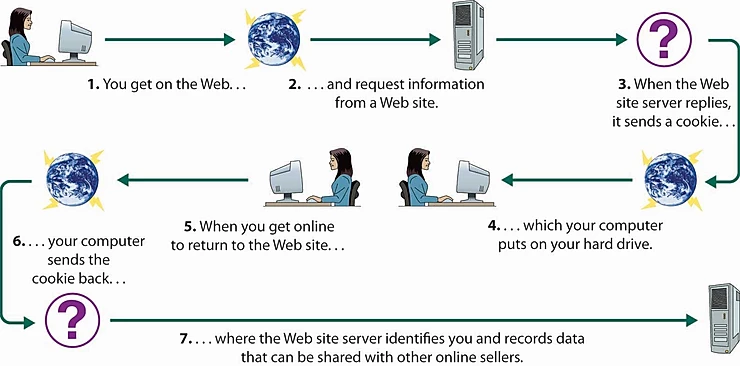
An HTTP cookie (web cookie, browser cookie) is a small piece of data that a server sends to the user's web browser. The browser may store it and send it back with later requests to the server.
Typically, it's used to tell if two requests came from the same browser.
Cookies are mainly used for three purposes:
-
Session management
Logins, shopping carts, game scores, or anything else the server should remember -
Personalization
User preferences, themes, and other settings -
Tracking
Recording and analyzing user behavior
The server issues a cookie to the client using the SET-COOKIE response header.
Set-Cookie: [cookie-name]=[cookie-value]
SetCookie: Tracking=wdr66gyU34pli89
When the user makes a subsequent request to the server, the cookie is added to the header.
HTTP Proxies
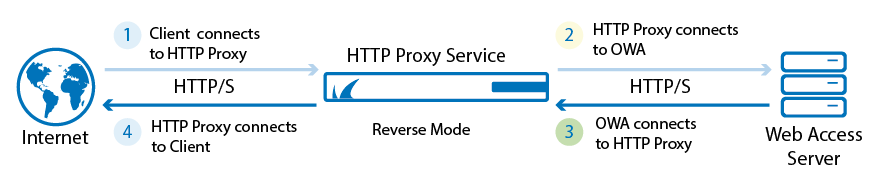
An HTTP proxy is a server between the client's browser and the web server.
When the clients browser is configured to use the HTTP proxy, all requests to the Internet must go first to the proxy. The proxy then forwards the request and receives the response before forwarding them to the client.
In this way, the HTTP proxy can provide access control, caching, authentication and content filtering.
HTTP Authentication
The HTTP protocol has its own mechanisms for authenticating users. These include:
-
Basic: sends user credentials as Base64-encoded string in request header
-
NTLM: challenge response mechanism
-
Digest: challenge response and uses MD5 check sums of a nonce with users credentials
The most common HTTP authentication is based on the "Basic" schema.
The general HTTP authentication framework
HTTP authentication framework is used by a server to challenge a client request and by a client to provide authentication information.
challenge - In security protocols, a challenge is some data sent to the client by the server in order to generate a different response each time.
The challenge and response flow works like this:

- The server responds to a client with a 401 (Unauthorized) response status and provides information on how to authorize with a WWW-Authenticate response header containing at least one challenge.
- A client that wants to authenticate itself with a server can then do so by including an Authorization request header field with the credentials.
- Usually a client will present a password prompt to the user and will then issue the request including the correct Authorization header.
The exchange must happen over an HTTPS (TLS) connection to be secure.